Starting a job in an office tends to be very stressful for an intern or a new employee, and the first day at the office could be particularly challenging. It takes time for the new staff to adjust and to grow familiar with other employees and their duties, and how they could be of assistance to the existing staff. Furthermore, it could take some time for new staff members to learn the ropes and their purpose within the office building, while understanding and learning how to use certain equipment, such as an automatic key lock or even just a coffee machine. Therefore, the app being proposed – Workplace Assisted Augmented Reality seeks to identify the users’ requirements for accomplishing a specific task within the workplace through user profiling and recommendation, whilst providing the relevant information for the users to learn and understand the environment around them via augmented reality (AR).
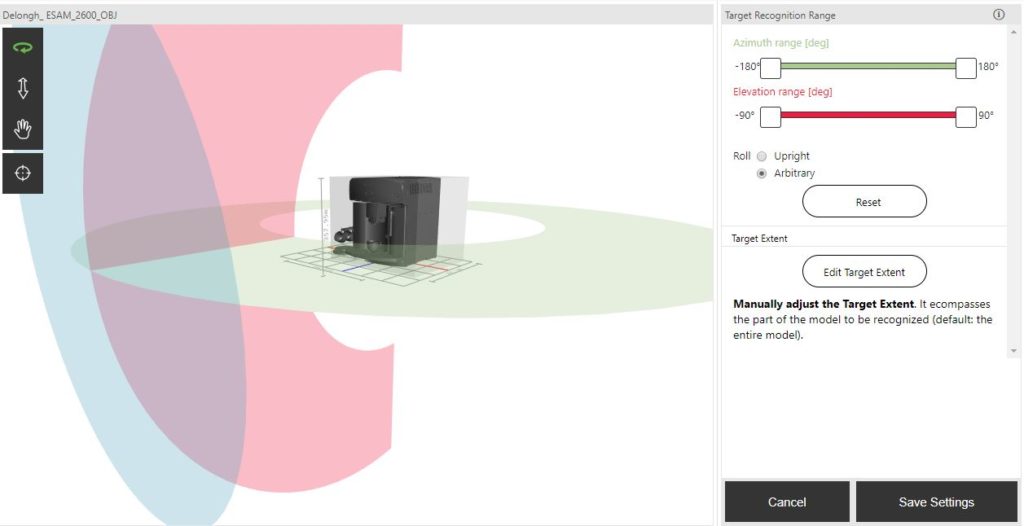
The application is intended to guide new employees through an adapted process that would enable them to understand the environment around them, the equipment they might use daily, and directions for easily finding their way between offices. It is also intended for guiding the users, by providing them with relevant information in order to succeed in their assigned task. The system incorporates collaborative filtering and a similarity-based technique using the SVD++ model and item-to-item-based similarity respectively, to provide recommendations ‒ along with deep learning and traditional computer-vision techniques using Vuforia ‒ to provide augmented reality.
Using the above-mentioned tools, the system provides information about offices, directions towards specific offices, and information on how to utilise the coffee machine of the company, for which the application was tailor-made..
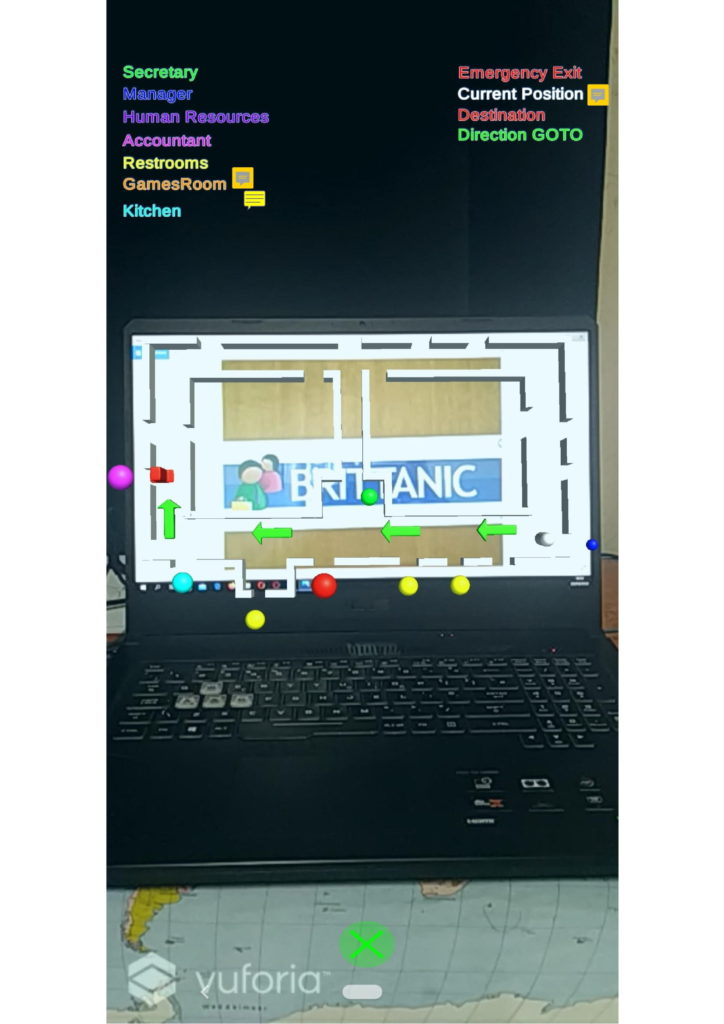
From the tests performed, the indication is that the SVD++ model was the most efficient for the AR environment in comparison to other machine learning models. SVD++ achieved an average root-mean-square error and mean absolute error of 3.1226 and 2.6866, respectively. The AR component achieved promising distance, colour, rotation and occlusion variance values. User evaluation results have given positive indications that the AR application was usable, useful and effective. In addition, this study proposes a number of recommendations on how this application might be improved further
Student: Gabriel Camilleri
Course: B.Sc. IT (Hons.) Artificial Intelligence
Supervisor: Dr. Vanessa Camilleri
